High blood sugar levels can lead to a range of health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and nerve damage. One way to manage high blood sugar is through diet, and a low-carb diet has been shown to be particularly effective. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of a low-carb diet for managing high blood sugar and provide tips on how to get started.
What is a Low-Carb Diet?
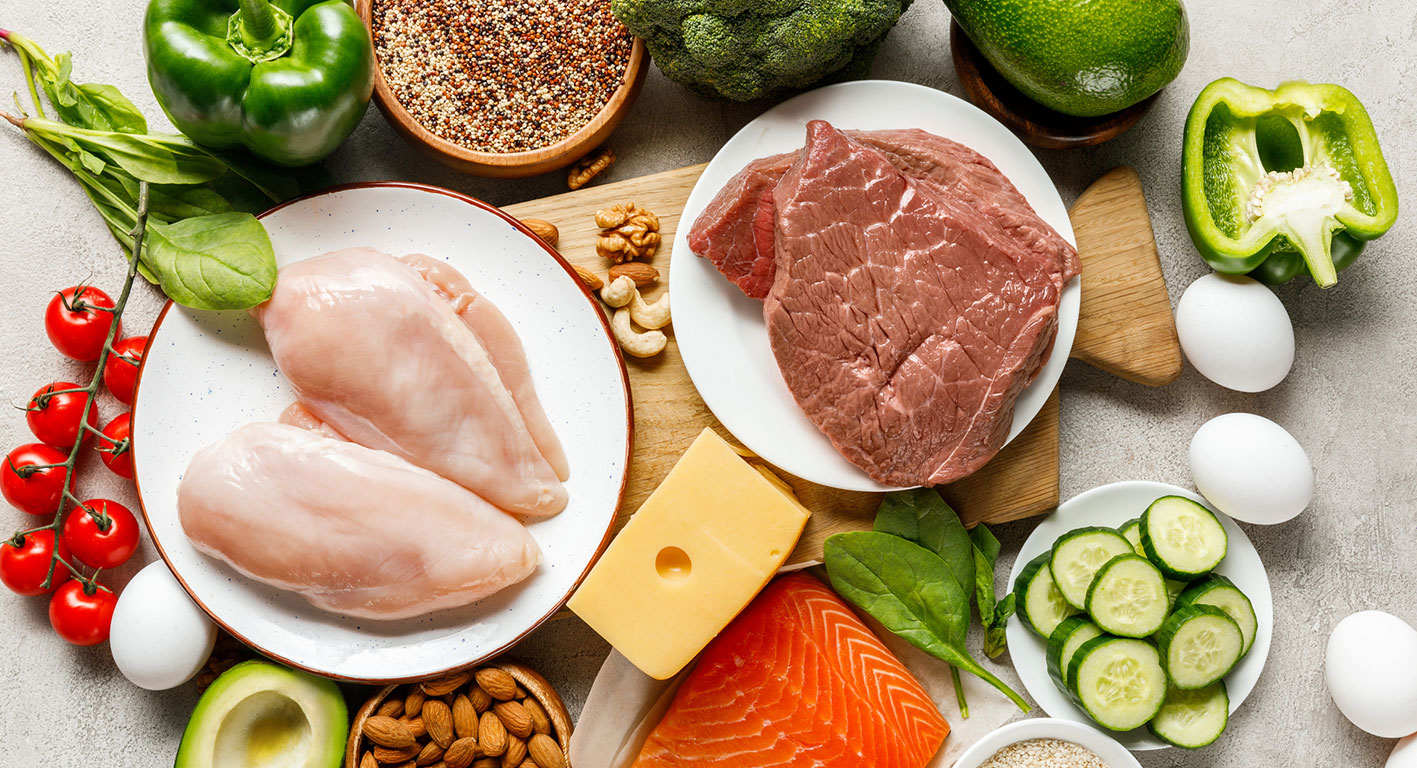
A low-carb diet is a diet that restricts carbohydrates, typically to around 50-150 grams per day, depending on the individual. This is in contrast to the standard American diet, which is often high in carbohydrates, particularly refined carbohydrates like sugar and white flour. A low-carb diet emphasizes protein, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables.

Benefits of a Low-Carb Diet for Managing High Blood Sugar
There are several benefits of a low-carb diet for managing high blood sugar:
- Lowering blood glucose levels: When you consume carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. A low-carb diet can help lower blood glucose levels by limiting the amount of glucose entering the bloodstream.
- Improving insulin sensitivity: Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance occurs when cells in the body become less responsive to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. A low-carb diet has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance.
- Reducing inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for many health problems, including diabetes. A low-carb diet can help reduce inflammation in the body by limiting the intake of pro-inflammatory foods like sugar and refined carbohydrates.
- Promoting weight loss: Excess weight is a risk factor for high blood sugar levels and diabetes. A low-carb diet can be an effective way to lose weight and maintain a healthy weight, which can help manage high blood sugar levels.
Getting Started with a Low-Carb Diet
If you’re interested in trying a low-carb diet to manage your high blood sugar, here are some tips to get started:
- Consult with your healthcare provider: Before starting any new diet, it’s important to talk with your healthcare provider, especially if you have diabetes or other health conditions.
- Choose healthy fats and proteins: Focus on healthy sources of fat and protein, such as avocado, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fish, chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of beef and pork.
- Choose non-starchy vegetables: Non-starchy vegetables are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, making them a great addition to a low-carb diet. Examples include leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, peppers, and mushrooms.
- Avoid refined carbohydrates: Foods like sugar, white flour, and processed snacks should be avoided on a low-carb diet, as they can spike blood sugar levels.
- Plan your meals and snacks: Planning your meals and snacks in advance can help you stick to a low-carb diet. Look for low-carb recipes and meal plans online, or consult with a registered dietitian for personalized advice.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels: If you have diabetes or prediabetes, it’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly while on a low-carb diet. This can help you adjust your diet and medication as needed.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is important for overall health and can also help manage blood sugar levels. Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day.
In conclusion, a low-carb diet can be a powerful tool for managing high blood sugar levels. By limiting carbohydrates and focusing on healthy fats, proteins, and non-starchy vegetables, you can help lower blood glucose levels, improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and promote weight loss. As always, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new diet or exercise regimen.